Getting Started with Excel: A Beginner’s Guide to Microsoft Excel
What is Microsoft Excel?
Let’s Getting Started with Excel. Microsoft Excel is a powerful spreadsheet software that allows users to store, organize, and analyse data in a tabular format. It is widely used in various industries, including business, education, and personal finance, to manage and track data.
History of Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel was first introduced in 1985 by Microsoft Corporation. Since then, it has become one of the most popular spreadsheet software in the world, with over 1 billion users worldwide.
Why Use Microsoft Excel?
Microsoft Excel offers a range of benefits, including:
- Easy data management and analysis
- Powerful formulas and functions
- Customizable charts and graphs
- Collaboration and sharing features
- Integration with other Microsoft Office applications
Setting Up Excel
Downloading and Installing Excel
To get started with Excel, you need to download and install it on your computer. You can download Excel as a standalone application or as part of the Microsoft Office suite.
System Requirements
Before installing Excel, make sure your computer meets the system requirements, including:
- Operating System: Windows 10 or macOS High Sierra or later
- Processor: 1.6 GHz or faster
- RAM: 4 GB or more
- Storage: 4 GB or more
Launching Excel for the First Time
Once you have installed Excel, launch it for the first time to set up your workspace. You will be prompted to sign in with your Microsoft account or create a new one.
Understanding the Excel Interface
The Excel Ribbon
The Excel ribbon is the topmost part of the Excel interface, consisting of several tabs, including Home, Insert, Page Layout, Formulas, Data, Review, and View.
The Worksheet
The worksheet is the main area where you enter and edit data. It consists of rows, columns, and cells.
The Formula Bar
The formula bar is located below the ribbon and displays the formula or value of the selected cell.
Basic Excel Concepts
Cells, Rows, and Columns
In Excel, data is stored in cells, which are arranged in rows and columns.
Cell References
Cell references are used to identify cells in formulas and functions. There are two types of cell references: relative and absolute.
Data Types
Excel supports several data types, including numbers, text, dates, and formulas.
Creating and Saving Workbooks
Creating a New Workbook
To create a new workbook, go to the File tab and click on New.
Saving a Workbook
To save a workbook, go to the File tab and click on Save As.
Workbook File Formats
Excel supports several file formats, including .xlsx, .xls, and .csv.
Entering and Editing Data
Entering Data
To enter data, simply click on a cell and start typing.
Editing Data
To edit data, click on a cell and make changes to the value or formula.
Data Validation
Data validation is a feature that allows you to restrict the type of data that can be entered in a cell.
Basic Formulas and Functions
Basic Arithmetic Operations
Excel supports basic arithmetic operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Functions
Functions are pre-built formulas that perform specific calculations, such as SUM, AVERAGE, and COUNT.
Formula Errors
Formula errors occur when there is an issue with a formula, such as a syntax error or a reference to a non-existent cell.
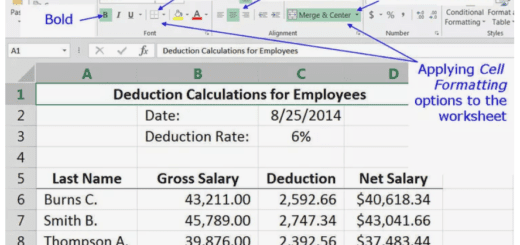
Formatting and Customizing Your Worksheet
Number Formatting
Number formatting allows you to change the way numbers are displayed in a cell, such as currency or date.
Alignment and Orientation
Alignment and orientation allow you to change the way text is displayed in a cell, such as left, center, or right alignment.
Conditional Formatting
Conditional formatting allows you to highlight cells based on specific conditions, such as values or formulas.
Working with Charts and Graphs
Creating a Chart
To create a chart, go to the Insert tab and click on Chart.
Chart Types
Excel offers several chart types, including Customizing Charts
You can customize charts by adding titles, labels, and legends.
Tips and Tricks for Beginners
Shortcuts and Hotkeys
Excel offers several shortcuts and hotkeys to improve productivity, such as:
- Ctrl+S to save a workbook
- Ctrl+Z to undo changes
- Ctrl+Y to redo changes
Excel Templates
Excel templates are pre-built workbooks that can be used to create common documents, such as budgets and invoices.
Excel Add-ins
Excel add-ins are third-party tools that can be installed to enhance Excel’s functionality, such as data analysis and visualization tools.
Conclusion
Congratulations on completing this comprehensive guide to getting started with Excel You now have a solid foundation in Excel and can start using it to manage and analyze data.
Next Steps
To continue improving your Excel skills, try the following:
- Practice using Excel regularly
- Experiment with new formulas and functions
- Watch online tutorials and videos
- Join online Excel communities and forums
Real-World Scenarios
Throughout this guide, we’ve used real-world scenarios to illustrate how Excel can be used in various industries, including:
- Personal finance: creating a budget and tracking expenses
- Business: managing inventory and tracking sales
- Education: grading and tracking student performance
Examples and Exercises
Throughout this guide, we’ve provided examples and exercises to help you practice and reinforce your learning. Try completing the exercises to improve your Excel skills.